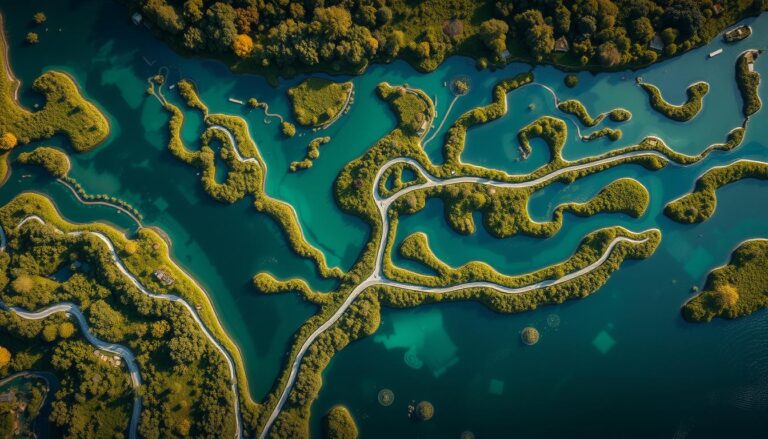
The National Hydrography Dataset Artificial Path is key for managing water resources. Its artificial path features are crucial. It gives us info on rivers, lakes, and wetlands, vital for water navigation and environmental management. The artificial path helps create detailed maps and models of water systems.
The artificial path is at the heart of the national hydrography dataset. It allows us to create detailed water system representations. The dataset is a vast collection of data on the nation’s surface water features. The artificial path is essential to this dataset.
The national hydrography dataset and its artificial path have many uses. They are important in environmental management, water navigation, and conservation. By using the hydrography dataset and its artificial path, we can make better decisions about water resources. The artificial path is a powerful tool for understanding and managing water systems.

Understanding the National Hydrography Dataset Artificial Path Basics
The National Hydrography Dataset Artificial Path is a detailed database of the nation’s surface water features. It includes artificial path features for water navigation and environmental management. These features are key to the hydrography dataset, offering insights into surface water locations, shapes, and attributes.
To grasp the NHD, we must explore its basics. This involves understanding its definition, core components, and historical development. Knowing its key features and limitations helps us see its uses and boundaries.
Definition and Core Components National Hydrography Dataset Artificial Path
The National Hydrography Dataset Artificial Path is a database that maps the nation’s surface water features, like rivers, lakes, and wetlands. It focuses on artificial path features, such as canals and dams. These are crucial for water navigation and human activities.
Historical Development of National Hydrography Dataset Artificial Path
The National Hydrography Dataset Artificial Path has evolved significantly, with ongoing efforts to enhance its accuracy and completeness. New technologies and data sources, like remote sensing and GIS systems, have improved the dataset.
Key Features and Characteristics National Hydrography Dataset Artificial Path
The NHD is a valuable resource for water navigation and environmental management. It offers detailed information on surface water features. It also supports various applications, from navigation to conservation.
The following table summarizes the NHD’s key features and characteristics:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Artificial path features | Canals, dams, and other human-made features |
| Hydrography dataset | Comprehensive database of surface water features |
| Water navigation | Facilitated through the use of artificial path features and other NHD components |
In conclusion, the NHD is a powerful tool for water navigation and environmental management. Its artificial path features and hydrography dataset offer valuable insights into the nation’s surface water features.
The Role of Artificial Paths in Water Navigation
Artificial paths are key in water navigation. They show the nation’s surface water features in detail. This info helps plan safe routes and avoid dangers. The hydrography dataset, with artificial paths, is a big help for water navigation.
Using artificial paths in water navigation has many benefits. It makes navigation safer, cheaper, and better for the environment. Users can spot hazards like shallow waters and narrow channels. This helps avoid accidents and protects the environment. Artificial paths are also crucial for emergency plans, helping in search and rescue.
Some main benefits of artificial paths in water navigation are:
- Improved navigation safety
- Reduced costs associated with navigation hazards
- Enhanced environmental management
- Increased efficiency in route planning
In summary, artificial paths are essential for safe and efficient water navigation. They help users make smart route choices and reduce risks in water navigation.
Technical Components of National Hydrography Dataset Artificial Path Data Structure
The National Hydrography Dataset (NHD) is a detailed database of the nation’s surface water features. It’s designed to give accurate and reliable info. Its technical parts are key for the dataset’s quality. The NHD works well with GIS systems for better water navigation and environmental management.
The NHD’s technical parts include data models and architecture. These help organize and store data. This setup lets the NHD show all the nation’s surface water features, like rivers, lakes, and wetlands. Using GIS systems with the NHD makes detailed maps and water feature analysis possible, which is vital for quality checks.
Data Models and Architecture National Hydrography Dataset Artificial Path
The NHD’s data models and architecture are made to be flexible and grow with data needs. They let the NHD handle many data types and sources, including spatial and attribute data. Working with GIS systems, the NHD can mix spatial and attribute data for better quality and analysis.
Integration with GIS Systems National Hydrography Dataset Artificial Path
When the NHD works with GIS systems, it makes detailed maps and analyzes water features. This is crucial for quality and analysis. It lets us use spatial and attribute data to understand water features. Also, it helps in making custom maps and analysis for environmental management and water navigation.
Quality Assurance Protocols National Hydrography Dataset Artificial Path
The NHD’s quality assurance protocols make sure the data is accurate and reliable. They include checks and verifications to find and fix data errors. Using GIS systems with the NHD also allows for custom quality checks. This is key for managing the environment and navigating waterways.
Applications in Environmental Management
The hydrography dataset is key in managing our environment, especially in saving water resources. It gives a detailed look at our surface water, helping us manage it better. This leads to cleaner water, less flood risk, and better protection of our ecosystems.
Here are some main ways the hydrography dataset helps in environmental management:
- Water resources management: It shows where water is scarce, helping us use it more wisely.
- Floodplain management: It gives us detailed info on floodplains, helping us manage flood risks better.
- Wetland conservation: It helps us find and protect wetlands, which are vital for many species and water quality.
Using the hydrography dataset is crucial for keeping our natural resources safe. As environmental management keeps improving, this dataset will become even more important. It will help us make better choices about our water resources.
In summary, the hydrography dataset has many important uses in environmental management. It gives us a detailed view of our surface water, helping us manage it better. This leads to cleaner water, less flood risk, and better protection of our ecosystems.
Advanced Analysis Techniques for Artificial Paths
Artificial paths in the National Hydrography Dataset (NHD) need special analysis to be fully useful. Spacial analysis helps us understand how surface water features connect with the environment. This knowledge leads to better data interpretation and smarter decisions.
Spacial analysis includes tools like spatial autocorrelation and spatial regression. These tools help spot patterns and trends in the data. This way, we can better use the NHD. For instance, we can find where to apply optimization approaches to enhance water quality.
Good data interpretation is key to getting the most out of the NHD. By using data visualization and statistical analysis, we can uncover important insights. Here are some effective strategies for data interpretation:
- Identify patterns and trends in the data
- Analyze relationships between variables
- Use data visualization to communicate findings
By using these strategies, we can unlock the NHD’s full potential. Optimization approaches help make the NHD more accurate and effective. This leads to better water navigation and environmental management.
| Technique | Description |
|---|---|
| Spatial Autocorrelation | Analysis of spatial relationships between variables |
| Spatial Regression | Analysis of relationships between variables in space |
| Data Visualization | Use of visual representations to communicate data insights |
Best Practices for Data Management
Effective data management is key to keeping the hydrography dataset reliable. It means doing regular quality assurance checks. This ensures the data is accurate and consistent. By following best practices, users can keep their dataset current and trustworthy.
Some top practices for managing data include:
- Regular data quality checks
- Secure data storage
- Standardized data sharing protocols
These steps help avoid data mistakes. They make sure the hydrography dataset is both accurate and reliable.
By sticking to these practices, users can manage their hydrography dataset well. This is vital for making smart choices in areas like environmental management and water navigation. Good data management is essential for the success of any project that uses the hydrography dataset.
Future Trends and Developments
The National Hydrography Dataset Artificial Path is set for big changes soon. Emerging technologies like artificial intelligence and machine learning will lead the way. These tools could make the dataset more accurate and efficient, helping with water navigation and environmental care.
There are many potential improvements on the horizon. These include higher spatial resolution, better data quality, and easier data sharing. These updates will be key in meeting the growing need for precise hydrographic data.
Experts predict the National Hydrography Dataset Artificial Path will remain vital for water navigation and environmental management. As new technologies emerge, the dataset will link up with other systems. This will give us a deeper understanding of our water resources.
Here are some major trends and developments expected for the National Hydrography Dataset Artificial Path:
- More use of artificial intelligence and machine learning for better data
- Better data sharing to help everyone work together
- Linking with other datasets and technologies for a fuller view of our water resources
The future of the National Hydrography Dataset Artificial Path is bright. New technologies and improvements will bring big changes to the field.
Conclusion
The National Hydrography Dataset (NHD) and its artificial paths are key in water navigation and environmental care. As it grows, it’s helping in many ways. It makes our waterways safer and supports important environmental projects.
The NHD’s future looks bright. New tech like GIS and data analytics will bring more insights. Teams from different fields will work together to keep the NHD leading-edge.
The NHD’s role in protecting our water and environment will grow. With its help, our waterways will be safer. Our ecosystems will thrive, and we’ll understand our water resources better than ever.
FAQ
What is the National Hydrography Dataset (NHD)?
The National Hydrography Dataset (NHD) is a detailed database. It shows the nation’s surface water features like rivers, lakes, and wetlands. It’s key for navigating water and managing the environment.
What are artificial path features in the NHD?
Artificial path features in the NHD give a full view of the nation’s surface water. This includes rivers, lakes, and wetlands. They’re vital for safe and efficient water travel and environmental care.
How are artificial paths used in water navigation?
Artificial paths in the NHD are crucial for water travel. They offer a detailed look at the nation’s water features. This makes navigation safer, cheaper, and better for the environment.
What are the technical components of the NHD data structure?
The NHD’s technical parts include data models and architecture. It also integrates with GIS systems and has quality checks. These ensure the dataset’s accuracy and trustworthiness.
How is the NHD used in environmental management?
The NHD is used a lot in environmental management. It helps with water resources, floodplains, and wetlands. It gives a clear picture of the nation’s water, aiding in better environmental care.
What are some advanced analysis techniques for artificial paths?
Advanced methods for artificial paths include spatial analysis and data interpretation. These help use the NHD better for water travel and environmental care.
What are the best practices for data management of the NHD?
Good data management for the NHD includes quality checks and secure storage. It also involves sharing data in a standard way. This keeps the dataset reliable and trustworthy.
What are some future trends and developments for the NHD?
The NHD’s future includes new tech like AI and machine learning. There might be better spatial resolution and data quality. Experts think the NHD will keep being key for water travel and environmental care.
